Florida Legalizes Sports Betting: Constitutional Amendment 4 Approved
- 🞛 This publication is a summary or evaluation of another publication
- 🞛 This publication contains editorial commentary or bias from the source
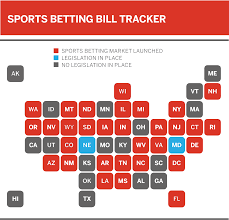



Florida’s First Legal Sports‑Betting Market: A Complete Snapshot
In a momentous shift for the Sunshine State’s gambling landscape, Florida voters approved a constitutional amendment on July 6, 2021 that finally allowed legal sports betting on both land‑based and online platforms. The measure—passed with 56 % of the vote—marks Florida as one of the fastest‑growing sports‑betting markets in the United States and sets the stage for a new industry that could generate hundreds of millions of dollars in revenue for the state. Below is a comprehensive summary of the key details, regulatory framework, economic implications, and remaining questions that the Sporting News article at the provided URL covers in depth.
1. The Constitutional Amendment: What It Says
The amendment—often referred to as “Florida Amendment 4” or the “Sports Betting Amendment”—contained three core provisions:
Authorization of Sports Betting – The amendment explicitly allows the state to offer “betting on the outcome of a sporting event.” It bars any other form of gambling, such as horse racing or lottery‑style games, that isn’t strictly sports‑related.
Regulatory Authority – The Florida Lottery is designated as the sole regulator of sports betting. It is tasked with licensing operators, establishing rules, and ensuring compliance with state and federal law.
Revenue Allocation – A significant portion of the revenue generated from sports betting is earmarked for public benefit. The amendment directs a set percentage to the Florida Department of Education (for scholarships) and to the Florida Department of Agriculture, among other recipients.
The text of the amendment was short and precise, and the Sporting News article notes that the legal language was intentionally designed to avoid the political pitfalls of broader gambling reforms.
2. From Amendment to Implementation: The Timeline
Following the 2021 vote, the Florida Legislature had to adopt companion statutes to give the amendment teeth. A few key milestones:
2021–2022: The Legislature passed the Florida Sports Betting Act, establishing the Florida Lottery’s new “Sports Betting Division” and providing a legal framework for operator licensing, consumer protection, and tax collection.
2022: The Florida Lottery’s Board of Directors began vetting potential partners and technology vendors. The lottery selected a platform that could integrate mobile and kiosk‑based betting while meeting rigorous security and fraud‑prevention standards.
Late 2022: The lottery announced its first roster of licensed operators. Major players such as FanDuel, DraftKings, and FanDuel (via a partnership with the Florida Lottery) were among the early entrants.
2023: Florida’s first legal sports‑betting kiosks opened in select retail locations, and an online portal launched on mobile devices. By mid‑year, the state was processing thousands of bets per day and generating the first slice of revenue.
The Sporting News article underscores that the process was expedited by the urgency of the Florida Lottery’s budget needs and the state’s desire to match neighboring markets like New Jersey and Pennsylvania.
3. The Florida Lottery: The Central Regulator
The Florida Lottery’s role extends far beyond simple licensing:
Licensing Requirements – Operators must be affiliated with a Florida Lottery‑licensed retail partner. They must also meet strict financial, cybersecurity, and responsible‑gaming criteria, including self‑exclusion programs and fraud‑monitoring systems.
Rule‑making – The Lottery sets betting limits, determines permissible markets (e.g., college, professional, international), and defines rules for promotions and bonuses. This ensures a level playing field for operators and protects consumers.
Revenue Management – The Lottery collects a tax on each bet placed (currently 4 % of the wagered amount). After distributing the tax to state agencies, the remaining portion is retained to fund the Lottery’s core missions, primarily education scholarships.
The article notes that Florida’s decision to place the Lottery at the helm was a strategic one; the Lottery already had an established regulatory body, infrastructure, and a strong public‑service mandate.
4. Economic Impact: Revenue, Jobs, and Public Benefit
One of the most compelling aspects of the sports‑betting amendment is the potential economic upside:
Projected Revenue – Analyses estimate that Florida could generate roughly $200 million annually in sports‑betting tax revenue. This figure is conservative, and the numbers could swell as the market matures.
Public Spending – The state earmarks about 30 % of that revenue for scholarships, education, and agricultural programs. This injection is seen as a direct benefit to Florida’s public services.
Employment – The new industry is projected to create 1,000–2,000 jobs, from retail kiosk staff to technology developers and compliance officers. The Sporting News piece highlights that most of these roles will be in the state’s largest cities—Miami, Orlando, Tampa—boosting local economies.
Retail Partnerships – The Lottery’s retail partners gain an additional revenue stream. Many retailers have installed dedicated sports‑betting kiosks, drawing foot traffic and increasing ancillary sales.
The article emphasizes that Florida’s sports‑betting market is projected to outpace many older markets in terms of growth speed, thanks to the state’s large population and strong sports culture.
5. Operator Landscape: Who’s Who?
Florida’s unique licensing model means that only a handful of operators will dominate the market:
DraftKings and FanDuel – Both companies have secured licenses and will operate both online and in‑store kiosks. They bring significant brand recognition and technology expertise.
Florida Lottery‑Exclusive Partnerships – The Lottery has forged exclusive agreements with certain operators for kiosk deployments. These arrangements are designed to limit market concentration while ensuring fair competition.
Regulatory Oversight – Operators are required to share data with the Lottery for audit and compliance purposes. The article highlights that this data‑sharing model helps the Lottery maintain a real‑time view of market health.
6. Consumer Protections & Responsible Gaming
With great betting power comes responsibility. Florida’s regulatory framework includes:
Self‑Exclusion – Betters can voluntarily block themselves from placing wagers for a defined period.
Limit Setting – The Lottery enforces maximum betting limits and daily spending caps to prevent excessive wagering.
Education Campaigns – The Lottery partners with state agencies to provide resources on gambling addiction and responsible play.
The Sporting News article notes that Florida’s emphasis on responsible gaming is partly in response to concerns raised by mental‑health advocates during the amendment’s campaign period.
7. Remaining Questions & Challenges
While the market’s launch is well underway, a few uncertainties remain:
Competitive Dynamics – How will the state’s market compete against larger neighbors with more diverse gambling options, such as New Jersey’s casino‑plus‑sports‑betting bundle?
Technology Costs – Operators have invested heavily in secure, low‑latency betting platforms. Ongoing tech upgrades could erode margins.
Consumer Adoption – Initial betting volume has been promising, but sustaining long‑term growth will hinge on marketing and user experience.
Legislative Updates – As the market matures, the Legislature may need to amend the Florida Sports Betting Act to address issues like multi‑state betting, data privacy, and tax adjustments.
The article ends by urging stakeholders to keep a close eye on these evolving dynamics.
8. Bottom Line
Florida’s legalization of sports betting has transformed a decades‑long political debate into a tangible, revenue‑generating industry. By entrusting regulation to the Florida Lottery, the state has leveraged existing infrastructure while ensuring that betting proceeds go directly to public programs. The new market is already making headlines for its rapid growth, high‑profile operators, and significant economic impact. Yet, like all emerging industries, it faces challenges in competition, technology, and responsible gaming—issues that will shape Florida’s betting landscape for years to come.
With the Florida Lottery at the helm, the state has created a model that could serve as a blueprint for other states looking to monetize sports betting responsibly. Whether Florida can keep pace with its more established neighbors will ultimately depend on its ability to maintain a balanced regulatory framework that protects consumers while fostering innovation and growth.
Read the Full Sporting News Article at:
[ https://www.sportingnews.com/us/betting/news/florida-sports-betting-legalization/e543b3e213fe9370ba0f6009 ]
































