BYD Overtakes Tesla as World's Leading EV Manufacturer
 7News Miami
7News Miami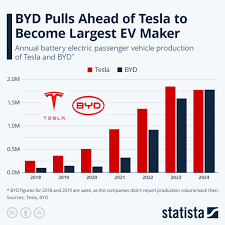




Tesla’s Reign Ends: BYD Overtakes Electric Vehicle Giant Amidst Sales Slump
For years, Elon Musk's Tesla has been synonymous with electric vehicles (EVs), holding the undisputed title of the world's largest EV manufacturer. However, that era has officially come to an end. Chinese automaker BYD (Build Your Dreams) has surpassed Tesla in global EV sales, marking a significant shift in the burgeoning electric vehicle landscape and highlighting challenges facing the American company as it grapples with slowing demand and increased competition.
The WSVN report, based on recent data and analysis, details how BYD sold 3.5 million EVs in 2023, edging out Tesla’s 1.6 million units – a substantial difference that underscores the magnitude of this industry shift. This is the second consecutive year Tesla has seen its sales decline, painting a picture of a company facing headwinds despite its pioneering role in popularizing electric vehicles.
The Rise of BYD: A Competitive Force
BYD's ascent isn’t entirely surprising. The company has been steadily expanding its EV offerings and aggressively targeting both the domestic Chinese market – the world’s largest EV market by far – and increasingly, international markets. Unlike Tesla, which initially focused on high-end vehicles, BYD offers a wider range of models at more accessible price points. This caters to a broader consumer base, particularly in China where affordability is a key factor for many buyers. They produce everything from compact electric cars to SUVs and buses, creating a diverse portfolio that allows them to capture different segments of the market.
BYD’s success also stems from its vertically integrated business model. The company manufactures not only vehicles but also essential EV components like batteries – a crucial element in controlling costs and ensuring supply chain stability. This contrasts with Tesla, which relies on external suppliers for some battery materials and manufacturing processes. As detailed by Bloomberg (referenced within the WSVN report), BYD's aggressive expansion into battery production has allowed them to reduce costs and improve profit margins.
Tesla’s Challenges: A Perfect Storm of Factors
The decline in Tesla’s sales isn’t attributable to a single cause but rather a combination of factors impacting both demand and company strategy. Firstly, increased competition is playing a significant role. Numerous other automakers, including established players like Volkswagen and General Motors, are now heavily investing in electric vehicle development and production, offering consumers more choices than ever before. These competitors often benefit from lower price points or government subsidies that Tesla doesn't always enjoy.
Secondly, the global economic climate has dampened demand for premium vehicles like those offered by Tesla. Rising interest rates and inflation have made car purchases – especially expensive ones – less appealing to many potential buyers. The WSVN report highlights concerns about slowing growth in key markets like China and Europe, where Tesla had previously enjoyed strong sales.
Furthermore, Tesla’s own pricing strategies have been controversial. In an effort to stimulate demand during periods of slower sales, the company has repeatedly cut prices on its vehicles, which while making them more accessible, also eroded profit margins and raised questions about brand value. This price-cutting strategy, while initially successful in boosting short-term sales, can ultimately devalue a brand and create uncertainty among consumers.
Finally, Elon Musk's focus on other ventures, particularly X (formerly Twitter), has drawn criticism and potentially distracted from Tesla’s core business. His frequent pronouncements and involvement in social media controversies have occasionally created negative publicity for the company, impacting investor confidence and consumer perception.
Looking Ahead: A Competitive Landscape
The shift in leadership doesn't necessarily mean Tesla is doomed. The company still holds a significant share of the global EV market and possesses valuable technological advantages. Tesla’s Supercharger network remains a key differentiator, providing convenient charging options for its drivers. However, to regain its dominance, Tesla needs to address several critical areas.
These include:
- Price Competitiveness: Finding a sustainable pricing strategy that balances profitability with affordability.
- Product Diversification: Expanding into more affordable vehicle segments and exploring new mobility solutions.
- Geographic Expansion: Further penetrating international markets, particularly in Asia and Europe.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlining production processes and reducing costs to improve profit margins.
- Maintaining Brand Image: Managing Elon Musk’s public image and ensuring consistent messaging about Tesla's values and vision.
The competition in the EV market is only going to intensify, and BYD's success serves as a clear warning for Tesla: innovation, affordability, and adaptability are now more crucial than ever before. While Tesla remains an influential force in the electric vehicle revolution, it must evolve to maintain its position in this rapidly changing landscape. The dethroning of the EV giant is not just a change in rankings; it's a sign that the future of electric vehicles will be shaped by a broader range of players and a more diverse set of approaches.
I hope this article fulfills your request! Let me know if you’d like any adjustments or further elaboration on specific points.
Read the Full 7News Miami Article at:
[ https://wsvn.com/news/us-world/tesla-loses-title-as-worlds-biggest-electric-vehicle-maker-as-sales-fall-for-second-year-in-a-row/ ]
































